Common Procedures
Regular Exams and Cleanings
Regular exams are an important part of maintaining your child's oral health. During your child’s regular exam, we will:
- Check for any problems that may not be seen or felt
- Look for cavities or any other signs of tooth decay
- Inspect the teeth and gums for gingivitis and signs of periodontal disease
- Perform thorough teeth cleaning
Your child’s exam will take about 45 minutes. Each regular exam includes a detailed teeth cleaning, in which we will clean, polish, and rinse the teeth to remove any tartar and plaque that have built up on the tooth’s surface.
Visiting our office every six months gives you the chance to talk to the doctor about any questions you may have about your child’s oral health. Regular exams are offered by appointment only, so please contact our practice today to schedule your child’s next dental exam and teeth cleaning.
Bonding
 Bonding is a conservative way to repair slightly chipped, discolored, or crooked teeth. During dental bonding, a white filling is placed onto your child's tooth to improve its appearance. The filling “bonds” with the tooth, and because it comes in a variety of tooth-colored shades, it closely matches the appearance of your child's natural teeth.
Bonding is a conservative way to repair slightly chipped, discolored, or crooked teeth. During dental bonding, a white filling is placed onto your child's tooth to improve its appearance. The filling “bonds” with the tooth, and because it comes in a variety of tooth-colored shades, it closely matches the appearance of your child's natural teeth.
Tooth bonding can also be used for fillings instead of amalgam. Many patients prefer bonded fillings because the white color is much less noticeable than silver. Bonding fillings can be used on front or back teeth, depending on the location and extent of tooth decay.
Bonding is less expensive than other cosmetic care and can usually be completed in one visit to our office. However, bonding can stain and is easier to break than other cosmetic care, such as porcelain veneers. If it does break or chip, tell your doctor. The bonding can generally be easily patched or repaired in one visit.
Crowns
 Crowns are a restorative procedure used to improve a tooth’s shape or to strengthen a tooth. Crowns are most often used for teeth that are broken, worn, or have portions destroyed by tooth decay.
Crowns are a restorative procedure used to improve a tooth’s shape or to strengthen a tooth. Crowns are most often used for teeth that are broken, worn, or have portions destroyed by tooth decay.
A crown is a “cap” cemented onto an existing tooth that usually covers the portion of the tooth above the gum line. In effect, the crown becomes the tooth’s new outer surface. Crowns can be made of porcelain, metal, or both. Porcelain crowns are most often preferred because they mimic the translucency of natural teeth and are very strong.
Crowns or onlays (partial crowns) are needed when there is insufficient tooth strength remaining to hold a filling. Unlike fillings, which apply the restorative material directly into the mouth, a crown is fabricated away from the mouth. A crown is created in a lab from your child's unique tooth impression, which allows a dental laboratory technician to examine all aspects of your child's bite and jaw movements. The crown is then sculpted just for your child so that his or her bite and jaw movements function normally once the crown is placed.
Extractions
 There are times when it is necessary to remove a tooth. Sometimes a baby tooth has misshapen or long roots that prevent it from falling out as it should, and the tooth must be removed to make way for the permanent tooth to erupt. At other times, a tooth may have so much decay that it puts the surrounding teeth at risk of decay, so the doctor may recommend its removal. Infection, orthodontic correction, or problems with a wisdom tooth can also require removal of a tooth.
There are times when it is necessary to remove a tooth. Sometimes a baby tooth has misshapen or long roots that prevent it from falling out as it should, and the tooth must be removed to make way for the permanent tooth to erupt. At other times, a tooth may have so much decay that it puts the surrounding teeth at risk of decay, so the doctor may recommend its removal. Infection, orthodontic correction, or problems with a wisdom tooth can also require removal of a tooth.
When it is determined that a tooth needs to be removed, your child’s dentist may extract the tooth during a regular checkup or may request another visit for this procedure. The root of each tooth is encased within the jawbone in a “tooth socket”, and the tooth is held in that socket by a ligament. In order to extract a tooth, the dentist must expand the socket and separate the tooth from the ligament holding it in place. While this procedure is typically very quick, it is important to share with the doctor any concerns or preferences for sedation.
Fillings
 Traditional dental restoratives, or fillings, may include gold, porcelain, or composite. Newer dental fillings include ceramic and plastic compounds that mimic the appearance of natural teeth. These compounds, often called composite resins, are typically used on the front teeth where a natural appearance is important. There are two different kinds of fillings: direct and indirect. Direct fillings are fillings placed directly into a prepared cavity in a single visit. Indirect fillings generally require two or more visits. These fillings include inlays, and veneers fabricated with ceramics or composites.
Traditional dental restoratives, or fillings, may include gold, porcelain, or composite. Newer dental fillings include ceramic and plastic compounds that mimic the appearance of natural teeth. These compounds, often called composite resins, are typically used on the front teeth where a natural appearance is important. There are two different kinds of fillings: direct and indirect. Direct fillings are fillings placed directly into a prepared cavity in a single visit. Indirect fillings generally require two or more visits. These fillings include inlays, and veneers fabricated with ceramics or composites.
Fluoride
 Fluoride is effective in preventing cavities and tooth decay and in preventing plaque from building up and hardening on the tooth’s surface. Fluoride care in a dentist’s office takes just a few minutes. After the care, your child may be asked not to rinse, eat, or drink for at least 30 minutes in order to allow the teeth to absorb the fluoride. Depending on your child’s oral health or the doctor’s recommendation, fluoride care may be required every three, six, or 12 months.
Fluoride is effective in preventing cavities and tooth decay and in preventing plaque from building up and hardening on the tooth’s surface. Fluoride care in a dentist’s office takes just a few minutes. After the care, your child may be asked not to rinse, eat, or drink for at least 30 minutes in order to allow the teeth to absorb the fluoride. Depending on your child’s oral health or the doctor’s recommendation, fluoride care may be required every three, six, or 12 months.
Mouthguards
 Whether your child wears braces or not, protecting his or her smile while playing sports is essential. Mouthguards help protect the teeth and gums from injury. If your child participates in any kind of full-contact sport, the American Dental Association recommends that he or she wear a mouthguard. Choosing the right mouthguard is essential. There are three basic types of mouthguards: the pre-made mouthguard, the “boil-and-bite” fitted mouthguard, and a custom-made mouthguard from the dentist. When you choose a mouthguard, be sure to pick one that is tear-resistant, comfortable and well-fitted for your mouth, easy to keep clean, and does not prevent your child from breathing properly. Your dentist can show your child how to wear a mouthguard properly and how to choose the right mouthguard to protect his or her smile.
Whether your child wears braces or not, protecting his or her smile while playing sports is essential. Mouthguards help protect the teeth and gums from injury. If your child participates in any kind of full-contact sport, the American Dental Association recommends that he or she wear a mouthguard. Choosing the right mouthguard is essential. There are three basic types of mouthguards: the pre-made mouthguard, the “boil-and-bite” fitted mouthguard, and a custom-made mouthguard from the dentist. When you choose a mouthguard, be sure to pick one that is tear-resistant, comfortable and well-fitted for your mouth, easy to keep clean, and does not prevent your child from breathing properly. Your dentist can show your child how to wear a mouthguard properly and how to choose the right mouthguard to protect his or her smile.
Sealants
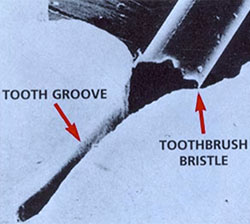 Did You Know: Pit and fissure cavities account for approximately 80-90% of all cavities in permanent posterior teeth and 44% in primary (baby) teeth. The groove in the electronic photomicrograph (right) is a typical pit and fissure found in both primary and permanent teeth.
Did You Know: Pit and fissure cavities account for approximately 80-90% of all cavities in permanent posterior teeth and 44% in primary (baby) teeth. The groove in the electronic photomicrograph (right) is a typical pit and fissure found in both primary and permanent teeth.
 The chewing surface of a primary molar before and after sealant placement (left) Sealant is a material placed into the pits and fissures on the chewing surfaces of the teeth. This “seals” out food particles that could get caught in the teeth, causing cavities. Sealants do not require the use of local anesthetic. Sealants reduce the risk of cavities in those pits and fissures. Placement of resin-based sealants in children and adolescents has shown a reduction of cavity incidence of 86%.
The chewing surface of a primary molar before and after sealant placement (left) Sealant is a material placed into the pits and fissures on the chewing surfaces of the teeth. This “seals” out food particles that could get caught in the teeth, causing cavities. Sealants do not require the use of local anesthetic. Sealants reduce the risk of cavities in those pits and fissures. Placement of resin-based sealants in children and adolescents has shown a reduction of cavity incidence of 86%.